Our latest featured trial is NCT03015623, which was registered in January 2017 but started recruiting patients in June 2017. In this trial, patients with acute kidney injury have their blood filtered through a device that holds mesenchymal stem/stromal cells from allogeneic bone marrow.
 It is well established that Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells (MSC) have excellent capacity to modulate the immune system in vivo1-3. This has led to numerous clinical reports where MSC were used to suppress auto-immune disorders4 or reduce the inflammation associated with injuries5.
It is well established that Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells (MSC) have excellent capacity to modulate the immune system in vivo1-3. This has led to numerous clinical reports where MSC were used to suppress auto-immune disorders4 or reduce the inflammation associated with injuries5.
Unfortunately, numerous animal trials have shown that when MSC are delivered intravenously they migrate very quickly to the lungs6-7. Alternate routes of MSC administration can bypass the lungs, but none seems to result in widespread dissemination or survival of MSC8-9. The good news is that the observed benefits of MSC therapy are primarily from the paracrine effect and do not require MSC engraftment, but the bad news is that it is hard to deliver sustained MSC therapy to an entire organ system.
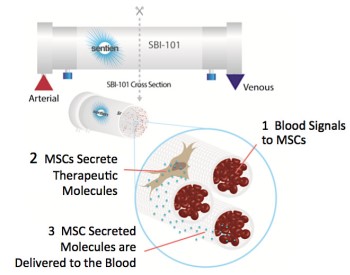
Clinical trial NCT03015623 provides a clever alternate solution: instead of bringing the MSC to the patient’s blood, the patient’s blood is brought to the MSC. In this trial, the patient’s blood is filtered through an extracorporeal bioreactor that combines two components: allogeneic human mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) and an FDA-approved plasmapheresis device. The SBI-101 device was patented by inventor Biju Parekkadan, PhD and is being developed by Sentien Biotechnologies, a company he co-founded to bring the technology to the clinic.
This initial trial demonstrates the safety of the Sentien technology platform for patients who are already receiving extracorporeal blood filtration (dialysis) for acute kidney injury. The number of cells in the SBI-101 device and the duration of treatment are fixed. In phase 2 the device will be tested against a sham control. Measures of SBI-101 efficacy could be reduced patient time on dialysis or reduced patient time in the ICU.
We believe that extracorporeal blood filtration is a promising method of delivering advanced cell therapy, and we are curious to follow the results of this trial.
References:
- Nauta AJ and Fibbe WE. Blood. 2007; 110(10):3499-506. Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stromal cells.
- Caplan AI and Correa D. Cell Stem Cell. 2011; 9(1):11-5. The MSC: an injury drugstore.
- Bernardo ME and & Fibbe WE. Cell Stem Cell 2013; 13(4):392–402. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: Sensors and Switchers of Inflammation
- Bersenev A, Couto PS, and Verter F. April 2016 newsletter of Parent’s Guide to Cord Blood Foundation Cell Therapy Clinical Trials for AutoImmune Diagnoses 2011-2015
- Centeno CJ, Al-Sayegh H, Freeman MD, Smith J, Murrell WD, Bubnov R. International Orthopaedics. 2016; 40(8):1755-65. A multi-center analysis of adverse events among two thousand, three hundred and seventy two adult patients undergoing adult autologous stem cell therapy for orthopaedic conditions.
- Harting MT, Jimenez F, Xue H, Fischer UM, Baumgartner J, Dash PK, Cox CS. J Neurosurg. 2009; 110(6):1189-97. Intravenous mesenchymal stem cell therapy for traumatic brain injury.
- Park SE, Lee NK, Lee J, Hwang JW, Choi SJ, Hwang H, Hyung B, Chang JW, Na DL. Neuroreport. 2016; 27(4):235-41. Distribution of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells in the Alzheimer's disease transgenic mouse after a single intravenous injection.
- Argibay B, Trekker J, Himmelreich U, Beiras A, Topete A, Taboada P, Pérez-Mato M, Vieites-Prado A, Iglesias-Rey R, Rivas J, Planas AM, Sobrino T, Castillo J, Campos F. Sci Rep. 2017; 7:40758. Intraarterial route increases the risk of cerebral lesions after mesenchymal cell administration in animal model of ischemia.
- Meseguer-Olmo L, Montellano AJ, Martínez T, Martínez CM, Revilla-Nuin B, Roldán M, Mora CF, López-Lucas MD, Fuente T. Nucl Med Biol. 2017; 46:36-42. Intraarticular and intravenous administration of 99MTc-HMPAO-labeled human mesenchymal stem cells (99MTC-AH-MSCS): In vivo imaging and biodistribution.